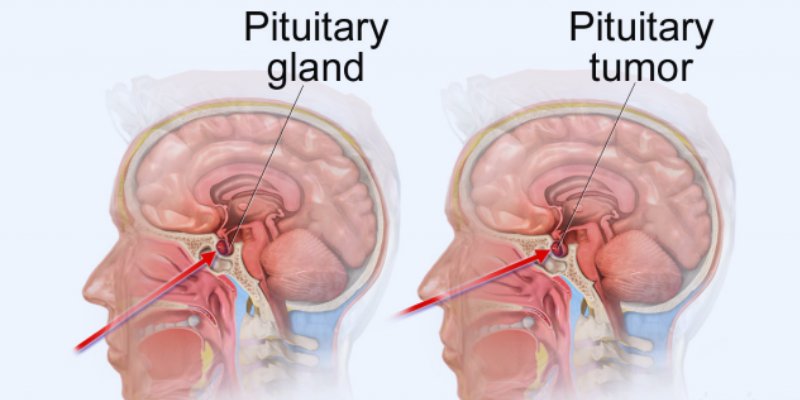
Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths that develop in the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain behind the nose, and its primary purpose is to release different types of hormones to perform various body functions. A pituitary tumor causes the pituitary gland to release many more hormones than it needs or too few to function correctly. These tumors are benign, which means they are harmless, and they are often referred to as adenomas.
Adenomas stay within or around the pituitary gland and don't spread to other body parts or adjacent areas. There are various ways to treat pituitary tumors, and they can also be removed through surgery. In addition, the growth of tumors can be controlled via radiation therapy or medications. Though pituitary tumors are not life-threatening, even then, it is crucial to know their underlying causes and related complications. So, let's learn it all here!
What Are The Causes of Pituitary Tumors?
Multiple factors, or a singular one, can cause pituitary tumors. You can confirm the cause once it is diagnosed and appropriately analyzed. The leading reason behind tumors is genetic mutations. Remember that your body adapts to external environments or conditions, causing cell division errors. Similarly, it happens due to specific changes within our body, such as the formation of cysts or the accumulation of cells at a particular place. In the case of pituitary tumors, the other leading causes are the following:
- Accidents, especially those that involve a head injury, chances are very high when your head gets hit.
- Bleeding around or in the pituitary area can be caused by external or internal factors.
- Some medications, especially cancer treatments, can also destabilize pituitary glands.
What Are The Symptoms Of Pituitary Tumors?
The size of the tumor and its location play a critical role in affecting or developing the symptoms. Besides that, the overproduction of the specific type of hormone by the tumor and the effect of the tumor on the normal production of other pituitary hormones also decide the symptoms one will witness. Generally, the common symptoms that one can identify and act upon promptly to get early diagnoses and start proper treatment are:
- Anxiety or depression
- Too much hair loss
- High blood pressure
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Feeling low energy
- Unusual growth patterns, either stunted growth or abrupt weight gains
- Vision changes
Whatever the symptoms, pituitary tumors are treatable; the treatment options vary depending on the functioning and non-functioning nature of the cancer. If the tumor functions, the hormone release and quantity can be controlled through medications. If it is non-functioning, the tumor can be removed through surgery or radiation therapy or controlled and managed by using both options.

What Are The Different Types Of Pituitary Tumors?
The pituitary adenomas are classified into the following categories:
Secretory Tumors or Functioning Adenomas:
Secretory tumors, also called functioning adenomas, can affect hormone production. Either the pituitary glands produce too many hormones other than needed, called hypersecretion, or they don't release too few hormones other than required, called hyposecretion. These tumors fall into the following categories:
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): The hormone is also known as ACTH, and these tumors are known as corticotroph adenomas. The hormone controls the body's response to stress levels and plays a vital role in managing other physiological processes like inflammation, metabolism, and immune function.
- Growth Hormone: This pituitary tumor, also called somatotroph adenomas, affects the release of hormones that grow in the body.
- Luteinizing Hormone And Follicle-Stimulating Hormone: LH or FSH hormones are crucial for your reproductive system. Pituitary tumors that affect the release of this hormone are called gonadotroph adenomas.
- Prolactin: This particular hormone is responsible for breast milk production and is needed for the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Pituitary tumors that affect their functioning are called prolactinomas or lactotroph adenomas.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone: This hormone stimulates the thyroid gland to produce hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development. Pituitary tumors that affect thyroid function are called thyrotrophin adenomas.
Nonsecretory or Non-Functioning Adenomas:
This type of pituitary tumor does not affect the functionality and quantity of hormone production, which is why it is referred to as a nonsecretory or non-functioning adenoma. Apart from hormone production, the size of the pituitary tumor starts expanding or enlarging from its actual size, which presses or puts pressure on the pituitary glands and other adjacent brain structures, causing constant headaches and vision problems.
Macroadenomas and Microadenomas
Adenomas can be either macroadenomas or microadenomas. If their size is greater than 1 centimeter, they are called macrocysts. Similarly, tumors whose size is less than 1 cm are called microadenomas. Both can be functioning or non-functioning.
Complications of Pituitary Tumors: An Understanding
Pituitary tumors can bring some serious complications that can affect the overall functioning of the body and can cause vision loss, bone loss, heart health issues, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and issues with memory and thinking. Besides that, the other complications that pituitary tumors can cause are:
- Pituitary Apoplexy is a rare complication that can occur if the tumor remains untreated. It can cause bleeding either in or out of the gland, and the risk of this bleeding depends on the size of the tumor. The symptoms of Pituitary apoplexy can be quick and life-threatening. They include severe headaches, lower blood pressure, and loss of peripheral vision.
- Seizures: When the pituitary tumor presses the medial temporal lobe (part of the brain), it can cause seizures. The seizures can cause changes in awareness, and you may seem awake. Also, you may not remember the seizures after they happened.
- Permanent Low Hormone Levels: If you are suffering from a pituitary tumor or a gland has been removed from your body, it will permanently change your hormonal levels. Therefore, patients need hormonal replacement therapy.
Conclusion:
Pituitary tumors or adenomas are tumors that affect the functioning of pituitary glands. These glands release multiple hormones that are essential for different body functions. From immune systems to managing body stress levels and reproductive systems, the release of appropriate quantities of these hormones is required for the proper functionality of these systems. Although these pituitary tumors are benign and rare, it is highly recommended to get a proper diagnosis and treatment. You must not ignore the abovementioned symptoms and get an MRI done after consulting your physician.